 There are several factors to consider when sizing your industrial dust collector, including facility space, application and particulate volume. Of course, the end-goal is to have an efficient industrial dust collector that keeps employees safe and your business running smoothly — but what other factors should you consider?
There are several factors to consider when sizing your industrial dust collector, including facility space, application and particulate volume. Of course, the end-goal is to have an efficient industrial dust collector that keeps employees safe and your business running smoothly — but what other factors should you consider?
That’s where air-to-cloth ratio comes in. This equation helps measure particulate volume against airflow and helps determine what size machine and filter you need in order to properly maintain clear airspace. We detail what air-to-cloth ratio is, how to calculate it and why it’s important for your business, below.
What is air-to-cloth ratio?
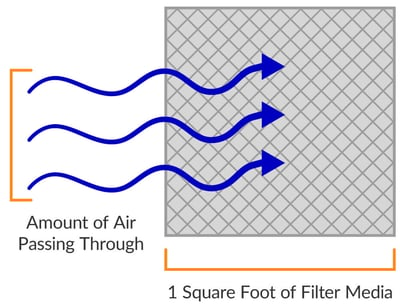
Also referred to as air-to-media ratio or filter velocity, air-to-cloth ratio quantifies the amount of air going through one square foot of filter media. It is often used as a simple way to state the ratio between cubic feet per minute (CFM) and square feet of filter area.
The more particulate that exists in each cubic foot of air filtering through the industrial dust collector, the lower the air-to-cloth ratio will need to be. Machines that capture the particulate at the source usually require a lower air-to-cloth ratio due to higher concentration.
Using the right filter matters, and there are two standard types of dust collector filters: bag and cartridge. Bag filters consist of cylindrical bags (or tubes) made of fabric that can handle a more demanding application with heavier dust, such as wood and grain dust. Cartridge filters are very efficient for fine dust and lighter loading applications, such as welding, plasma, laser and other fume or smoke applications. Because cartridge filters are pleated, they have a larger total filtering surface area per CFM, which reduces the air-to-cloth ratio and size of the dust collector.
How to calculate air-to-cloth ratio
To calculate air-to-cloth ratio for an A.C.T. dust collector, we take the amount of airflow (CFM) and divide it by the amount of filter area within that dust collector. For example, if a dust collector was moving 4,000 CFM and had 2,000 square feet of filter area, we could say that it had a 4,000-to-2,000 ratio. This can be simplified to a 2:1 air-to-cloth ratio.
Another example, this time on the lower ratio end, is if a dust collector was moving 2,000 CFM and had 2,000 square feet of filter media. Since they are the same number, the air-to-cloth ratio equals 1:1.
Why is air-to-cloth ratio important for industrial dust collection?
Air-to-cloth ratio is one of the more important factors in determining how long a filter will last in a given application. Although there are many factors that come into play when determining filter life, air-to-cloth ratios can give good guidance when determining the size of the dust collector required for a given amount of air.
Our experts will help you determine the right air-to-cloth ratio when selecting an industrial dust collector so that you’re not overspending while ensuring you’re overpreparing. If air-to-cloth ratio is too high, meaning there’s not enough filter media for the airflow and volume of particulate your application is producing, dust will actually enter the filters faster than they can keep up with. This will result in frequent filter clogging and reduce the life of your filter.
A lower air-to-cloth ratio will result in longer filter life and is often used in nuisance applications like laser cutting, blasting, metalworking and robotic welding, while a higher air-to-cloth ratio will result in shorter filter life and is often used when dust loading is very light.
A.C.T. Dust Collectors offers the ultimate in air filtration. Interested in learning more? Request a quote today and one of our experts will help you determine the best air-to-cloth ratio of bag and cartridge filters for your application.



























%20Collectors%20Image.png?width=143&height=143&name=ADC%20(Ambient)%20Collectors%20Image.png)




























.png?width=240&height=91&name=ACT%20Dust%20Collectors%20Logo%20Solid%20White%202020%20(1).png)
.png?width=148&height=149&name=usa-manufactured-dust-collectors%20(1).png)